[Avg. reading time: 7 minutes]
CoAP
Introduction
CoAP stands for Constrained Application Protocol, developed by the IETF. (Internet Engineering Task Force).
Constrained Environments
- Energy constraints.
- Memory limitations.
- Processing capibility.
- Unattended network operation.
- Unreliable networks.
- Higher Latency in communication.
Popular Examples:
- Small embedded devices.
- Runs on small capacity batteries.
- Minimum RAM/ROM.
Products
- Window / Door sensors.
- Healthcare Wearables.
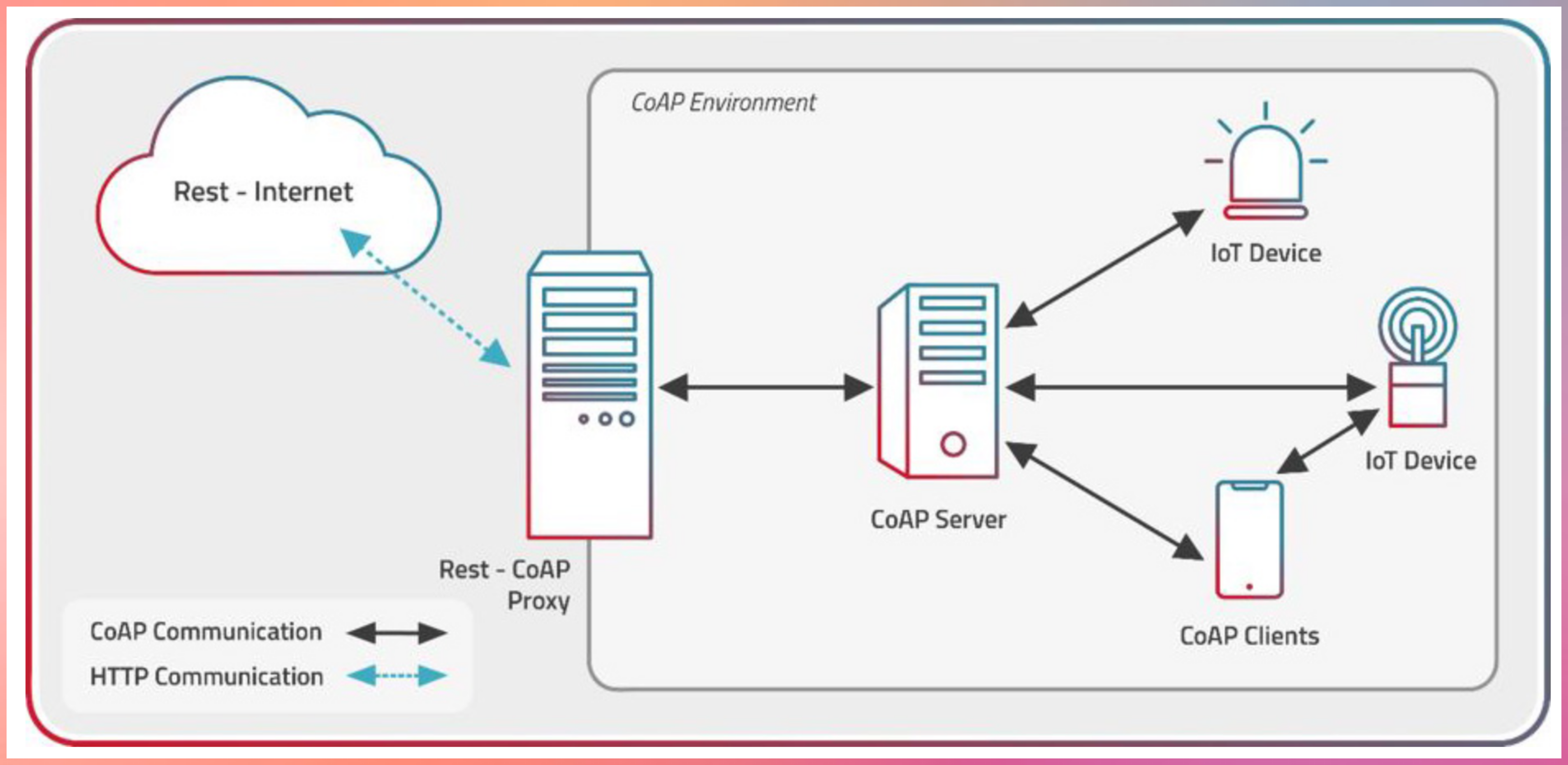
Key Features
Request-Response Model: CoAP operates on a request-response communication model, much like its counterpart HTTP. In this model, a client sends a CoAP request to a server, and the server responds with the requested data or action. CoAP’s request methods mirror those of HTTP, including GET, PUT, POST, and DELETE.
CoAP is like HTTP, but runs on UDP for better efficiency. HTTP is TCP-based, while CoAP targets smaller data exchanges.
Best used for applications wanting to read sensor data effectively.
Multicast Support: CoAP incorporates support for multicast communication, enabling a single CoAP message to be sent to multiple recipients simultaneously. Multicast communication reduces network traffic and efficiently disseminates data, a feature that aligns well with resource-constrained environments.
Layers in CoAP
-
Application Layer
-
Request / Response Layer
-
Message Layer
-
UDP Layer
-
Message & UDP are Lower Layers
-
Application and Request/Response are Upper Layers
Message Types
- Confirmable Messaging (CON)
- Non Confirmable Messaging (NON)
- Acknowledgeable Messaging (ACK)
- Reset Messaging (RST)
Features of CoAP
- Lightweight, asynchoronous and efficient with a 4-byte header.
- Runs connectionless on UDP, allowing for quick message exchanges.
- Easily integrates with HTTP for seamless web connectivity.
- Supports common methods: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, dealing with these aynchronously.
| Feature | MQTT | CoAP |
|---|---|---|
| Base Protocol | TCP | UDP |
| Security | SSL/TLS | DTLS (less common) |
| Reliability | High | Medium |
| Power Usage | Higher | Lower |
| Scalability | High | Medium |
| Message Model | Publish-Subscribe | Request-Response |
| Multicast | Limited | Supported |
| QoS Levels | Yes (3 levels) | No (basic) |
| Latency | Medium | Low |
| Communication Pattern | One-to-Many | One-to-One, One-to-Many |
| Standardization | OASIS Standard | IETF Standard |
| Complexity | Higher due to Broker Setup | Lower, simpler implementation |
| Use Cases | Real-time Data Transfer, Reliable Communication | Low-Power, Low-Bandwidth Applications |
Demo
git clone https://github.com/gchandra10/python_coap_examples.git