[Avg. reading time: 37 minutes]
InfluxDB
InfluxDB is schema-less.
InfluxDB is a purpose-built time series database designed to handle high volumes of timestamped data. It excels at collecting, storing, processing, and visualizing metrics and events from applications, IoT devices, and infrastructure monitoring systems.
- Easy to get started - just write data and InfluxDB handles the structure
- Flexible for evolving data requirements
- No database migrations needed when adding new fields or tags
Key Features
Time Series Optimized: Built from the ground up for time-stamped data, providing efficient storage and fast queries.
High Write Performance: Can handle millions of data points per second, making it ideal for real-time monitoring applications.
Flux Query Language: A powerful functional data scripting language for analytics, monitoring, and alerting.
Bucket Storage: Organizes data into buckets with customizable retention policies.
Downsampling & Retention: Automatically manages data lifecycle with features to aggregate older data and purge expired points.
Built-in UI: Comes with a comprehensive web interface for data visualization, dashboarding, and administration.
Data Model
Measurements: Similar to tables in relational databases (e.g., temperature, cpu_usage)
Tags: Indexed metadata for fast filtering (e.g., location=kitchen)
Fields: The actual data values being stored (e.g., value=22.5)
Timestamps: When each data point was recorded
Common Use Cases
IoT Sensor Data: Tracking environmental conditions, equipment performance
DevOps Monitoring: System metrics, application performance, infrastructure health
Real-time Analytics: Business metrics, user activity, performance trends
Financial Market Data: Stock prices, trading volumes, economic indicators
Epoch Time (https://epochconverter.com)
Installation
Cloud
Via Docker
mkdir influxdb
cd influxdb
mkdir data
mkdir config
podman run -d -p 8086:8086 \
--name myinflux \
-v "$PWD/data:/var/lib/influxdb2" \
-v "$PWD/config:/etc/influxdb2" \
-e DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_MODE=setup \
-e DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_USERNAME=admin \
-e DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_PASSWORD=P@ssw0rd1 \
-e DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_ORG=rowan \
-e DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_BUCKET=mybucket \
-e DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_RETENTION=1h \
influxdb:latest
At this time latest is Version 2.x Minimum Retention period is 1 hr
24h = 1 day
168h = 7 days
720h = 30 days
8760h = 1 year
Format of Sample Data
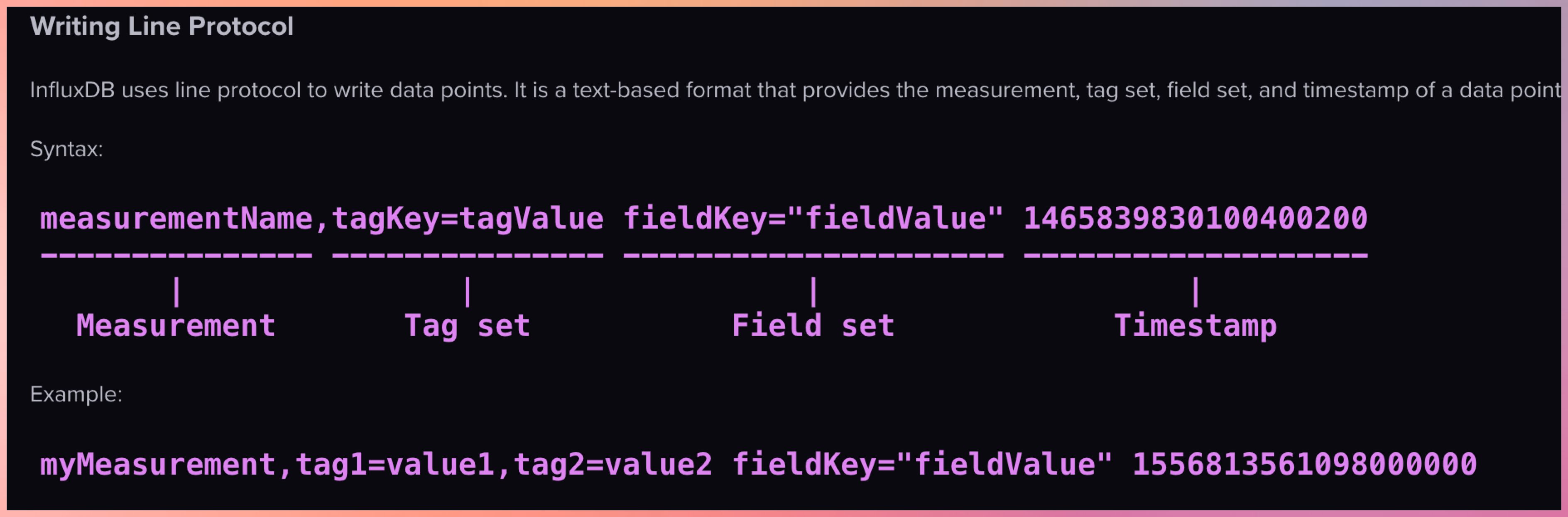
In InfluxDB, a “measurement” is a fundamental concept that represents the data structure that stores time series data. You can think of a measurement as similar to a table in a traditional relational database.
Note:
- Use singular form for measurement names (e.g., “temperature” not “temperatures”)
- Be consistent with tag and field names
- Consider using a naming convention (e.g., snake_case or camelCase)
Example 1
temperature,location=kitchen value=22.5
- temperature -> measurement
- location=kitchen -> tags
- value=22.5 -> field
- if TimeStamp is missing then it assumes current TimeStamp
Example 2
temperature,location=kitchen,sensor=thermometer value=22.5 1614556800000000000
Example 3
Multiple Tags and Multiple Fields
temperature,location=kitchen,sensor=thermometer temp_c=22.5,humidity_pct=45.2
- location=kitchen,sensor=thermometer -> Tags
- temp_c=22.5,humidity_pct=45.2 -> Field
Example 4
temperature,location=kitchen,sensor=thermometer reading=22.5,battery_level=98,type="smart",active=true
Load Data
Login via UI
http://localhost:8086
Username: admin Password: P@ssw0rd1
- Navigate to “Data” in the left sidebar, then select “Buckets”
- You should see your “mybucket” listed. Click on it.
- Look for “Add Data” button and select “Line Protocol”
Line Protocol
Line protocol, is InfluxDB’s text-based format for writing time series data into the database. It’s designed to be both human-readable and efficient for machine parsing.
temperature,location=kitchen value=22.5
temperature,location=living_room value=21.8
temperature,location=bedroom value=20.3
temperature,location=kitchen value=23.1
temperature,location=living_room value=22.0
temperature,location=bedroom value=20.7
temperature,location=kitchen value=22.8
temperature,location=living_room value=21.5
temperature,location=bedroom value=20.1
temperature,location=kitchen value=23.5
temperature,location=living_room value=21.9
temperature,location=bedroom value=19.8
temperature,location=kitchen value=24.2
temperature,location=living_room value=22.3
temperature,location=bedroom value=20.5
temperature,location=kitchen value=23.7
temperature,location=living_room value=22.8
temperature,location=bedroom value=21.0
temperature,location=kitchen value=22.9
temperature,location=living_room value=22.5
temperature,location=bedroom value=20.8
-
Click “Write Data” to insert these values
-
To verify your data was written, go to “Explore” in the left sidebar
-
Create a simple query using the query builder:
-
Select your “mybucket” bucket
-
Filter by measurement: “temperature”
-
Select fields: “value”
-
Group by: “location”
-
Click “Submit”
You should see a graph with your temperature readings for different locations.
Upload bulk data
Create a TEXT file with all the values and choose Upload File
Contents of the text file can be as-is.
humidity,location=kitchen value=45.2
humidity,location=living_room value=42.8
humidity,location=bedroom value=48.3
humidity,location=kitchen value=46.1
humidity,location=living_room value=43.5
humidity,location=bedroom value=49.1
humidity,location=kitchen value=45.8
humidity,location=living_room value=42.3
humidity,location=bedroom value=48.7
humidity,location=kitchen value=46.5
humidity,location=living_room value=44.2
humidity,location=bedroom value=49.8
humidity,location=kitchen value=47.2
humidity,location=living_room value=45.1
humidity,location=bedroom value=50.2
humidity,location=kitchen value=46.8
humidity,location=living_room value=44.8
humidity,location=bedroom value=49.6
humidity,location=kitchen value=45.9
humidity,location=living_room value=43.7
humidity,location=bedroom value=48.5
co2_ppm,location=kitchen value=612
co2_ppm,location=living_room value=578
co2_ppm,location=bedroom value=495
co2_ppm,location=kitchen value=635
co2_ppm,location=living_room value=582
co2_ppm,location=bedroom value=510
co2_ppm,location=kitchen value=621
co2_ppm,location=living_room value=565
co2_ppm,location=bedroom value=488
co2_ppm,location=kitchen value=642
co2_ppm,location=living_room value=595
co2_ppm,location=bedroom value=502
co2_ppm,location=kitchen value=658
co2_ppm,location=living_room value=612
co2_ppm,location=bedroom value=521
co2_ppm,location=kitchen value=631
co2_ppm,location=living_room value=586
co2_ppm,location=bedroom value=508
co2_ppm,location=kitchen value=618
co2_ppm,location=living_room value=572
co2_ppm,location=bedroom value=491
Create a CSV file
create iot.csv inside the data folder.
#datatype measurement,tag,tag,tag,double,long,string,boolean
measurement,location,sensor,type,reading,battery_level,status,active
temperature,kitchen,thermometer,smart,22.5,98,normal,true
temperature,living_room,thermometer,smart,21.8,97,normal,true
temperature,bedroom,thermometer,smart,20.3,96,normal,true
temperature,kitchen,thermometer,smart,23.1,95,normal,true
temperature,living_room,thermometer,smart,22.0,94,normal,true
temperature,bedroom,thermometer,smart,20.7,93,normal,true
humidity,kitchen,hygrometer,smart,45.2,97,normal,true
humidity,living_room,hygrometer,smart,42.8,96,normal,true
humidity,bedroom,hygrometer,smart,48.3,95,normal,true
co2_ppm,kitchen,air_quality,smart,612,99,normal,true
co2_ppm,living_room,air_quality,smart,578,98,normal,true
co2_ppm,bedroom,air_quality,smart,495,97,normal,true
Login to Client CLI
podman exec -it myinflux bash
ls /var/lib/influxdb2
you will see the iot.csv (magic ;))
More Info
https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/cloud/write-data/developer-tools/csv/
USE CLI
influx write -b mybucket -f iot.csv --format csv
ISO 8601 time format.
T: Starting for Time
Z: UTC
-05:00: EST
influx delete --bucket mybucket --start 2025-02-26T00:00:00Z --stop 2025-03-06T23:59:59Z
REST API
Uses HTTP-based communication to write data to InfluxDB.
Login to Portal and Generate a API Key.
GitBash / Mac / Linux
create another bucket mybucket2
export TOKEN="<your token>"
export BUCKET="mybucket2"
export ORG="rowan"
Note: Bucket and Org properties were defined in Container.
Measurement: CPU
This uses system DateTime when inserting data.
curl -i -XPOST "http://localhost:8086/api/v2/write?org=$ORG&bucket=$BUCKET&precision=s" \
--header "Authorization: Token $TOKEN" \
--data-raw "cpu,host=server01,region=us-west cpu_usage=45.2,cpu_temp=62.1,cpu_idle=54.8"
precision=s to specify seconds precision.
Date Time along with data
curl -i -XPOST "http://localhost:8086/api/v2/write?org=$ORG&bucket=$BUCKET" \
--header "Authorization: Token $TOKEN" \
--data-raw "cpu,host=server01,region=us-west cpu_usage=44.2,cpu_temp=60,cpu_idle=52 $(date +%s)000000000"
Measurement: Memory
curl -i -XPOST "http://localhost:8086/api/v2/write?org=$ORG&bucket=$BUCKET&precision=s" \
--header "Authorization: Token $TOKEN" \
--data-raw "memory,host=server01,region=us-west used_percent=72.1,available_mb=3945.7,total_mb=16384"
Combining Measurements
curl -i -XPOST "http://localhost:8086/api/v2/write?org=$ORG&bucket=$BUCKET&precision=s" \
--header "Authorization: Token $TOKEN" \
--data-raw "cpu,host=server02,region=us-central cpu_usage=22.2,cpu_idle=75.8
memory,host=server02,region=us-central used_percent=27.1,available_mb=14945.7,total_mb=24384"
curl -i -XPOST "http://localhost:8086/api/v2/write?org=$ORG&bucket=$BUCKET&precision=s" \
--header "Authorization: Token $TOKEN" \
--data-raw "cpu,host=server02,region=us-central cpu_usage=23.2,cpu_idle=76.8
memory,host=server02,region=us-central used_percent=28.1,available_mb=15945.7,total_mb=24384"
InfluxDB CLI
Install CLI
https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/cloud/tools/influx-cli/
FLUX Query Language
In InfluxDB 3.0 they are introducing SQL back.
influx query 'from(bucket: "mybucket")
|> range(start: -50m)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == "temperature") '
Python Examples
git clone https://github.com/gchandra10/python_influxdb_examples.git
Telegraf
Telegraf, a server-based agent, collects and sends metrics and events from databases, systems, and IoT sensors. Written in Go, Telegraf compiles into a single binary with no external dependencies–requiring very minimal memory.
export MQTT_HOST_NAME=""
export MQTT_PORT=
export MQTT_USER_NAME=""
export MQTT_PASSWORD=""
export INFLUX_TOKEN=""
export INFLUX_DB_ORG=""
export INFLUX_DB_BUCKET=""
telegraf.conf
# Global agent configuration
[agent]
interval = "5s"
round_interval = true
metric_batch_size = 1000
metric_buffer_limit = 10000
collection_jitter = "0s"
flush_interval = "10s"
flush_jitter = "0s"
precision = ""
debug = false
quiet = false
hostname = ""
omit_hostname = false
# MQTT Consumer Input Plugin
[[inputs.mqtt_consumer]]
servers = ["ssl://${MQTT_HOST_NAME}:${MQTT_PORT}"]
username = "${MQTT_USER_NAME}"
password = "${MQTT_PASSWORD}"
# Set custom measurement name
name_override = "my_python_sensor_temp"
# Topics to subscribe to
topics = [
"sensors/temp",
]
# Connection timeout
connection_timeout = "30s"
# TLS/SSL configuration
insecure_skip_verify = true
# QoS level
qos = 1
# Client ID
client_id = "telegraf_mqtt_consumer"
# Data format
data_format = "value"
data_type = "float"
# InfluxDB v2 Output Plugin
[[outputs.influxdb_v2]]
# URL for your local InfluxDB
urls = ["http://localhost:8086"]
# InfluxDB token
token = "${INFLUX_TOKEN}"
# Organization name
organization = "${INFLUX_DB_ORG}"
# Destination bucket
bucket = "${INFLUX_DB_BUCKET}"
# Add tags - match the location from your MQTT script
[outputs.influxdb_v2.tags]
location = "room1"
Run Telegraph
telegraf --config telegraf.conf --debug
Storing output in InfluxDB and S3
export MQTT_HOST_NAME=""
export MQTT_PORT=
export MQTT_USER_NAME=""
export MQTT_PASSWORD=""
export INFLUX_TOKEN=""
export INFLUX_DB_ORG=""
export INFLUX_DB_BUCKET=""
export S3_BUCKET=""
export AWS_REGION=""
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=""
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=""
telegraf.conf
# Global agent configuration
[agent]
interval = "5s"
round_interval = true
metric_batch_size = 1000
metric_buffer_limit = 10000
collection_jitter = "0s"
flush_interval = "10s"
flush_jitter = "0s"
precision = ""
debug = false
quiet = false
hostname = ""
omit_hostname = false
# MQTT Consumer Input Plugin
[[inputs.mqtt_consumer]]
servers = ["ssl://${MQTT_HOST_NAME}:${MQTT_PORT}"]
username = "${MQTT_USER_NAME}"
password = "${MQTT_PASSWORD}"
# Set custom measurement name
name_override = "my_python_sensor_temp"
# Topics to subscribe to
topics = [
"sensors/temp",
]
# Connection timeout
connection_timeout = "30s"
# TLS/SSL configuration
insecure_skip_verify = true
# QoS level
qos = 1
# Client ID
client_id = "telegraf_mqtt_consumer"
# Data format
data_format = "value"
data_type = "float"
# InfluxDB v2 Output Plugin
[[outputs.influxdb_v2]]
# URL for your local InfluxDB
urls = ["http://localhost:8086"]
# InfluxDB token
token = "${INFLUX_TOKEN}"
# Organization name
organization = "${INFLUX_DB_ORG}"
# Destination bucket
bucket = "${INFLUX_DB_BUCKET}"
# Add tags - match the location from your MQTT script
[outputs.influxdb_v2.tags]
location = "room1"
# S3 Output Plugin with CSV format
[[outputs.remotefile]]
remote = 's3,provider=AWS,access_key_id=${AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID},secret_access_key=${AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY},region=${AWS_REGION}:${S3_BUCKET}'
# File naming
files = ['{{.Name}}-{{.Time.Format "2025-03-26"}}']