[Avg. reading time: 5 minutes]
Types of Cloud
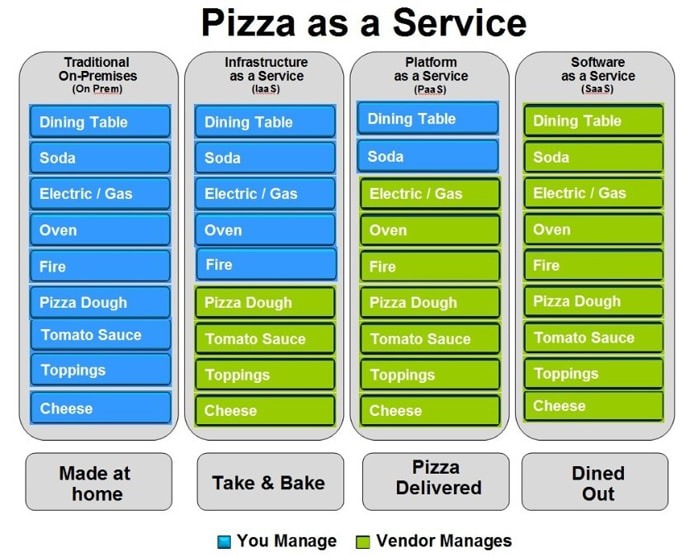
SaaS – Software as a Service
SaaS provides ready-to-use cloud applications. Example: Google Docs, Gmail. In IoT, it offers real-time dashboards, alerts, and analytics.
Pros
- No infrastructure management
- Fast deployment
- Built-in analytics and alerts
Cons
- Limited customization
- Possible vendor lock-in
- Data stored in vendor cloud
PaaS – Platform as a Service
PaaS provides the tools and services to build and deploy IoT apps, including SDKs, APIs, device management, rules engines, and ML pipelines.
Example: HiveMQ (MQTT)
Pros
- Scalable and customizable
- Device lifecycle and security handled
- Integration with ML, analytics tools
Cons
- Learning curve
- Requires cloud expertise
- Still dependent on vendor ecosystem
IaaS – Infrastructure as a Service
IaaS gives you virtual machines, storage, and networking. In IoT, it lets you build fully custom pipelines from scratch.
Example: Virtual Machine
Pros
- Full control over environment
- Highly customizable
- Can install any software
Cons
- You manage everything: scaling, patching, backups
- Not beginner-friendly
- Higher ops burden
FaaS – Function as a Service
FaaS lets you run small pieces of code (functions) in response to events, like an MQTT message or sensor spike. Also called serverless computing.
Example: AWS Lambda, Azure Functions
When a temperature sensor sends a value > 90°C to MQTT, a Lambda function triggers an alert and stores the value in a DB.
Pros
- No need to manage servers
- Scales automatically
- Event-driven and cost-effective
Cons
- Cold start delays
- Limited execution time and memory
- Stateless only