[Avg. reading time: 10 minutes]
Grafana
Grafana is an open-source analytics and visualization platform that allows you to query, visualize, alert on, and understand your metrics from various data sources through customizable dashboards.
- Provides real-time monitoring of IoT device data through intuitive dashboards
- Supports visualization of time-series data (which is common in IoT applications)
- Offers powerful alerting capabilities for monitoring device health and performance
- Enables custom dashboards that can display metrics from multiple IoT devices in one view.
- InfluxDB is optimized for storing and querying time-series data generated by IoT sensors.
- The combination provides high-performance data ingestion for handling large volumes of IoT telemetry.
- InfluxDB’s data retention policies help manage IoT data storage efficiently.
- Grafana can easily visualize the time-series data stored in InfluxDB through simple queries.
- Both tools are lightweight enough to run on edge computing devices for local IoT monitoring.
Deploy InfluxDB/Grafana
Create a network
- Isolation and security - The dedicated network isolates your containers from each other and from the host system, reducing the attack surface.
- Container-to-container communication - Containers in the same network can communicate using their container names (like “myinflux” and “mygrafana”) as hostnames, making connections simpler and more reliable.
- Port conflict prevention - You avoid potential port conflicts on the host, as multiple applications can use the same internal port numbers within their isolated network.
- Simpler configuration - Services can reference each other by container name instead of IP addresses, making configuration more maintainable.
podman network create monitoring-net
podman run -d --name myinflux \
--network monitoring-net \
-p 8086:8086 \
-v "$PWD/influxdb-data:/var/lib/influxdb2" \
-v "$PWD/influxdb-config:/etc/influxdb2" \
-e DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_MODE=setup \
-e DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_USERNAME=admin \
-e DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_PASSWORD=P@ssw0rd1 \
-e DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_ORG=rowan \
-e DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_BUCKET=mybucket \
influxdb:latest
podman run -d --name mygrafana \
--network monitoring-net \
-p 3000:3000 \
-v "$PWD/grafana-data:/var/lib/grafana" \
grafana/grafana-oss:latest
InfluxDB
http://localhost:8086
Grafana
http://localhost:3000
podman exec -it myinflux influx write \
--bucket mybucket \
--precision s \
"test_metric,host=server1 value=13.4 $(date +%s)"
podman exec -it myinflux influx write \
--bucket mybucket \
--precision s \
"test_metric,host=server1 value=13.6 $(date +%s)"
podman exec -it myinflux influx write \
--bucket mybucket \
--precision s \
"test_metric,host=server1 value=12.42 $(date +%s)"
podman exec -it myinflux influx write \
--bucket mybucket \
--precision s \
"test_metric,host=server1 value=13.1 $(date +%s)"
podman exec -it myinflux influx write \
--bucket mybucket \
--precision s \
"test_metric,host=server1 value=12.8 $(date +%s)"
podman exec -it myinflux influx write \
--bucket mybucket \
--precision s \
"test_metric,host=server1 value=12.5 $(date +%s)"
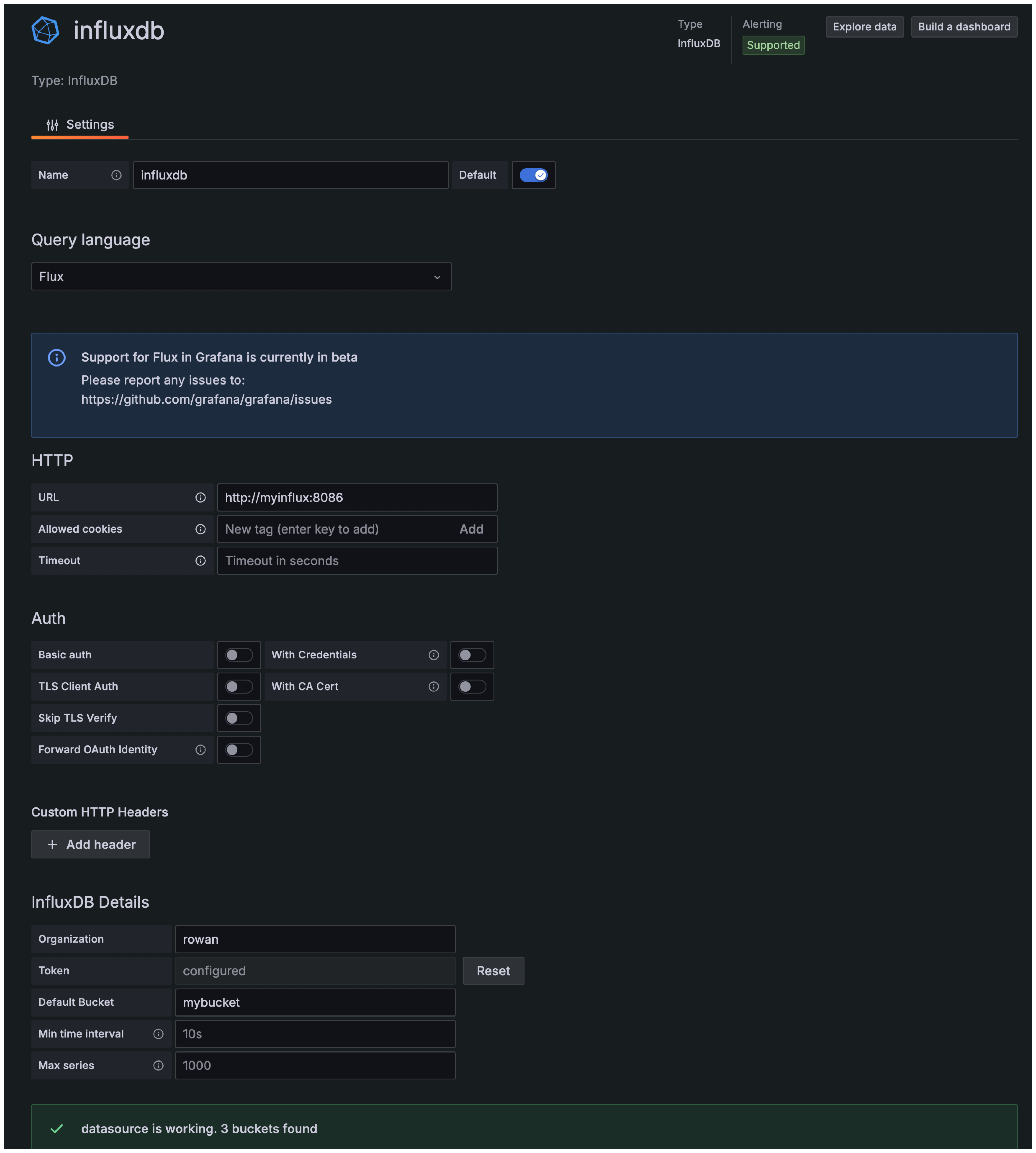
**Grafana > Alerting > Alert Rules **
- Select influxdb
- Create New Rule
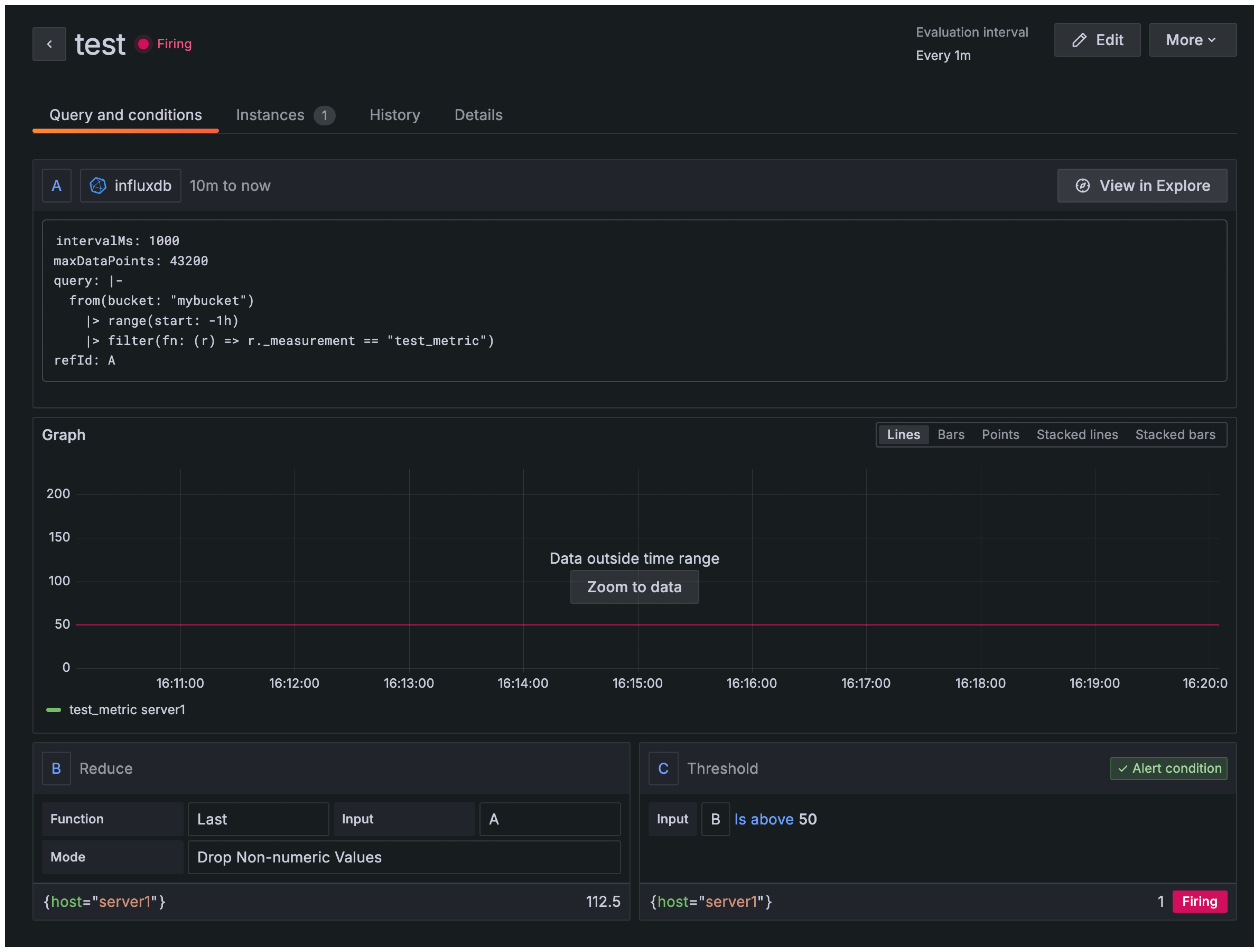
from(bucket: "mybucket")
|> range(start: -1h)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == "test_metric")
Use this query not the one shown in image
from(bucket: "mybucket")
|> range(start: -1h)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == "test_metric")
from(bucket: "mybucket")
|> range(start: -1h)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == "test_metric")
|> aggregateWindow(every: 5m, fn: mean, createEmpty: false)
|> yield(name: "mean")
````<span id='footer-class'>Ver 6.0.5</span>
<footer id="last-change">Last change: 2026-02-05</footer>````